What You Need to Know
Who is PJM?
PJM Interconnection is a regional transmission organization (RTO) that coordinates the movement of wholesale electricity in all or parts of Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee, Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia.
What is the PJM capacity auction and what are capacity costs?
To ensure system reliability, PJM relies on a capacity market. The capacity market functions through annual auctions where generators pledge to be available during a specified delivery year, which spans from June to May.
Capacity costs are payments made to power generators to guarantee their availability to produce electricity when needed, especially during peak demand periods. These costs are then distributed to electricity customers based on their contribution to the system’s peak demand. This guarantees sufficient power generation capacity is available to prevent blackouts and maintain grid stability during high usage periods.
What are Demand-Based Charges and Energy-Based Charges?
Demand-based (kW) charges and energy-based (kWh) charges are two primary elements of electricity bills.
Demand-Based Charges (kW): These charges are calculated based on the peak power usage (measured in kilowatts) at any single point in time. In PJM, capacity costs are associated with a customer’s Peak Load Contribution (PLC), which reflects their demand during the system’s highest demand hours from the previous year.
Energy-Based Charges (kWh): Energy charges depend on the total electricity consumption over a period (measured in kilowatt-hours). These charges account for the cost of producing and delivering the consumed electricity and are independent of the capacity needed to handle peak demand.
Why is there a significant rise in capacity costs?
PJM’s recent capacity auction saw a rise in costs due to:
- Decommissioning of Older Power Plants: The closure of outdated and less efficient plants has reduced the number of available resources.
- Increased Demand Forecasts: Economic expansion and the move towards electrification have led to higher electricity consumption.
- Changes in Regulations and Policies: More stringent environmental regulations are affecting generation capacity.
- Rising Generator Expenses: Inflation and supply chain disruptions have increased the costs of maintaining and developing power plants.
Strategies to Stay Ahead of Rising Costs
- Know Your Peak Usage: Customers are charged based on their contribution to the grid’s peak demand. Identify when your building consumes the most energy to adjust usage and prevent costly spikes.
- Budget for Demand Changes: Forecasting peak demand charges now helps you avoid surprise costs and keeps energy expenses predictable.
- Explore Demand Response Programs: Many utilities offer financial incentives for businesses that reduce energy use during peak periods.
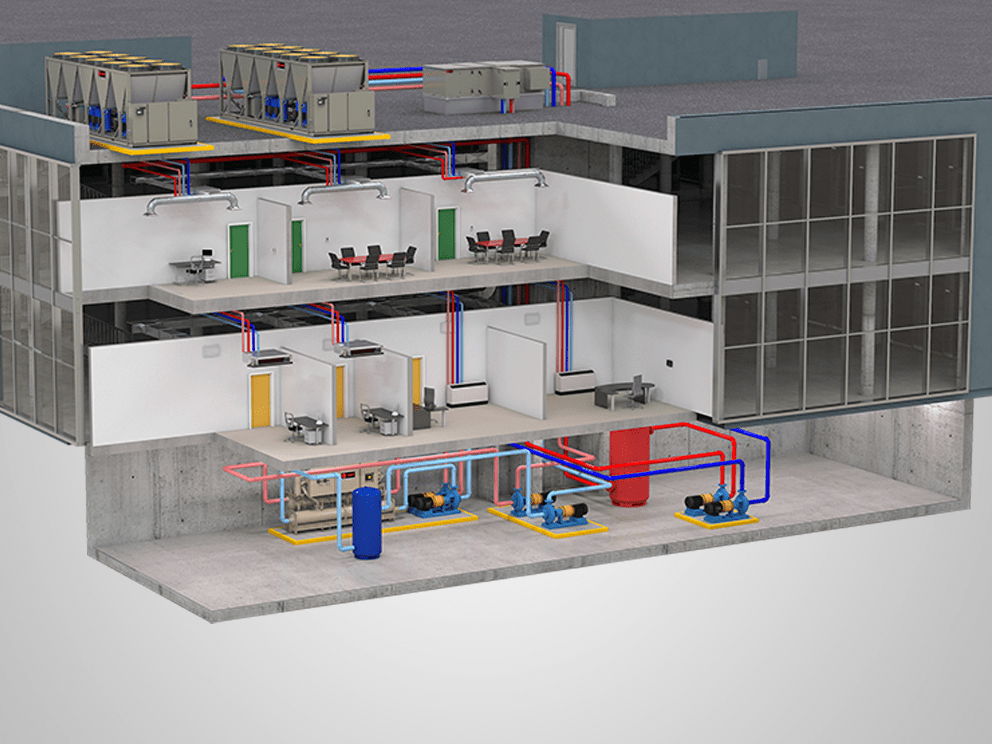
- Invest in Energy Efficient Upgrades: Upgrading to energy efficient technologies like LED lighting and updated HVAC systems can help reduce overall energy demand and usage.
- Load Shifting: Businesses can help to lower costs by rescheduling energy-intensive activities to off-peak hours when the grid demand is reduced.
- Battery Energy Storage Systems: On-site battery systems store energy during low demand and release it during peaks which help to reduce reliance on the grid during peak hours.
- On-Site Generation: Using on-site renewable energy or backup generators during peak times can help cut down on grid demand and save on capacity costs.
- Monitoring and Controls: Energy management systems deliver real-time data on energy consumption, allowing for precise control and quick response during peak demand periods.
Trane Can Help
Rising energy costs shouldn’t come at the expense of building performance. Trane experts can help you understand your energy demand, identify cost-saving opportunities, and create a building enhancement strategy tailored to your needs.